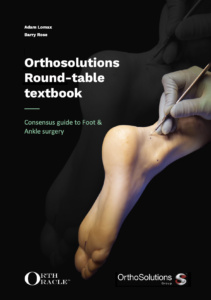
Cavovarus foot correction: Calcaneal and metatarsal osteotomies with tibialis posterior to peroneus brevis transfer
Overview
Subscribe to get full access to this operation and the extensive Foot Surgery Atlas.
Learn the Cavovarus foot correction: Calcaneal and metatarsal osteotomies with tibialis posterior to peroneus brevis transfer surgical technique with step by step instructions on OrthOracle. Our e-learning platform contains high resolution images and a certified CME of the Cavovarus foot correction: Calcaneal and metatarsal osteotomies with tibialis posterior to peroneus brevis transfer surgical procedure.
Pes Cavovarus describes a deformity of the foot characterised by a high arch, and a plantar-flexed 1st ray. Whilst some subtle deformities may represent a physiological normal variant, pes cavovarus is often associated with neurological disorders; the commonest being Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (Hereditary sensori-motor neuropathy).
The deformity progresses as a result of asymmetrical denervation of the flexor and extensor musculature. The power of the Gastocnemius-Soleus, Tibialis posterior and Peroneus Longus muscles are usually preserved relative to the Peroneus brevis, tibialis anterior and intrinsic foot muscles, which are demonstrably weak.
The driver for the deformity is usually a plantar flexion of the 1st metatarsal. In order to engage the ground, the rest of the forefoot compensates by an obligatory supination. The effect of the forefoot supination is (via the forefoot-hindfoot couple) an inversion of the hindfoot, producing the characteristic varus heel. The concept of contracture or tightness of the plantar fascia remains controversial.
In those patients with flexible deformity, joint preserving surgery can be considered and such a case is detailed here treated with osteotomies and tendon transfers.
Author: Mr Nick Cullen FRCS (Tr & Orth)
Institution: The Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital , Stanmore ,London ,UK.
Clinicians should seek clarification on whether any implant demonstrated is licensed for use in their own country.
In the USA contact: fda.gov
In the UK contact: gov.uk
In the EU contact: ema.europa.eu
Online learning is only available to subscribers.