Cervical Laminoplasty for treatment of Cervical spondylotic myelopathy
Overview
Learn the Cervical Laminoplasty for treatment of Cervical spondylotic myelopathy surgical technique with step by step instructions on OrthOracle. Our e-learning platform contains high resolution images and a certified CME of the Cervical Laminoplasty for treatment of Cervical spondylotic myelopathy surgical procedure.
Cervical spondylosis is a common age related degenerative process which may lead to development of axial neck pain, cervical radicular symptoms or cervical myelopathy. Most common levels are C5/6 followed by C6/7 because they are associated with the most flexion and extension in the subaxial spine.
Degenerative cervical spondylosis is the most common cause of cervical myelopathy. It is a slowly progressive disorder usually caused by spinal cord compression and ischaemia due to age related changes in the spine.
Although asymptomatic degeneration of the cervical spine is common in the elderly, when these changes lead to myelopathy, patients are at risk of motor, sensory and autonomic dysfunction, as well as a reduction in quality of life. Cervical myelopathy is generally considered a surgical disorder due to its natural history. Surgery may arrest progression and can improve neurological outcomes.
The decision to use either an anterior, posterior or combined anterior-posterior surgical approach depends on many factors. The cervical spinal cord may be compressed from a single, or by multi level, anterior based, posterior based or circumferentially from combined anterior and posterior based pathologies. The contribution each of the aforementioned pathologies make to overall cervical cord compression will also vary.
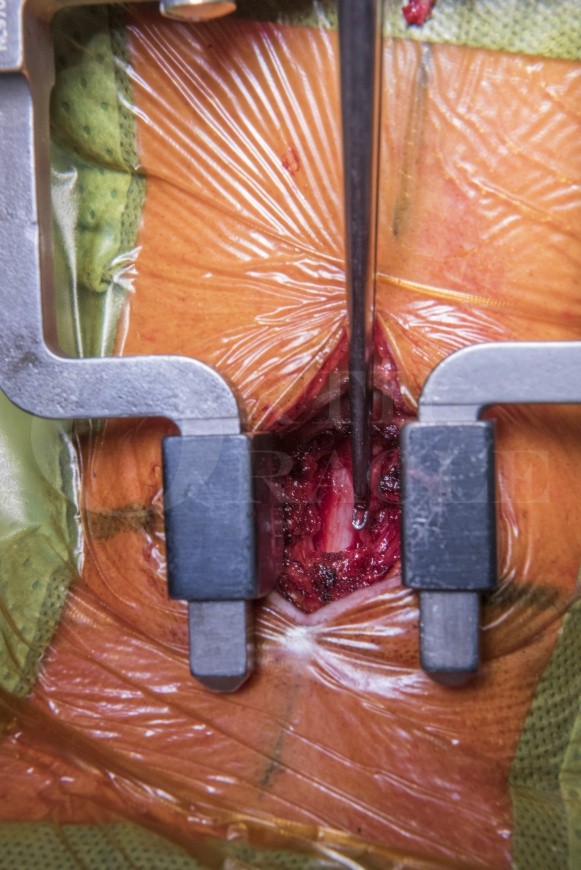
Here I perform a C4 split cervical laminoplasty to decompress the spinal cord at C3/4.
The technique described is in a patient with a C1 (Jefferson) fracture and C2 Type II peg fracture treated conservatively due to a life threatening cardiac event immediately post injury. An MRI at that admission did not demonstrate any cervical stenosis.
Follow-up Computer Tomography (CT) imaging demonstrated union of the C1 fracture, but the C2 peg fracture did not radiologically unite.
At 12-month review he had clinical features suggestive of cervical myelopathy and imaging showed a new C3/4 stenosis compressing the spinal cord rather than C1/C2 instability. The patients past medical history included oropharangeal carcinoma treated with surgery and radiotherapy that had already resulted in difficulties with swallowing and speech. I therefore opted to manage his Cervical spondylotic Myelopathy (CSM) with posterior decompression of the cord, via a split cervical laminoplasty technique. This technique for decompressing the spinal cord posteriorly is both discussed and demonstrated in the technique.
Author: Neil Upadhyay FRCS(Tr & Orth)
Institution: The Avon Orthopaedic Centre, Bristol, UK.
Clinicians should seek clarification on whether any implant demonstrated is licensed for use in their own country.
In the USA contact: fda.gov
In the UK contact: gov.uk
In the EU contact: ema.europa.eu
Online learning is only available to subscribers.