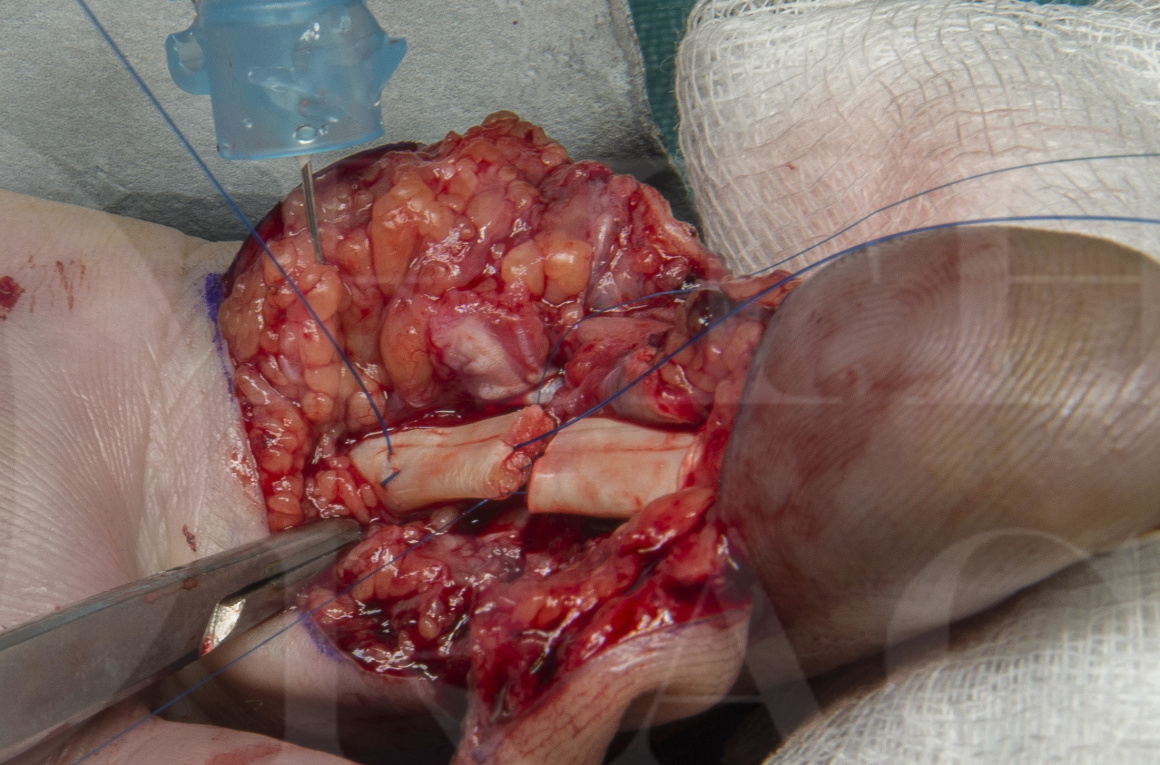
Flexor tendon: Zone 2 repair
Overview
Subscribe to get full access to this operation and the extensive Upper Limb & Hand Surgery Atlas.
Learn the Flexor tendon: Zone 2 repair surgical technique with step by step instructions on OrthOracle. Our e-learning platform contains high resolution images and a certified CME of the Flexor tendon: Zone 2 repair surgical procedure.
Primary repair of a lacerated flexor tendon is a technically demanding procedure that requires careful exposure of the tendon ends with minimal disruption to adjacent structures, meticulous tissue handling and accurate coaptation with a robust suture repair.
A sound repair should therefore allow institution of an early active rehabilitation protocol allowing early tendon gliding, intrinsic healing with minimal scarring and restoration of normal finger motion. Most flexor tendon repairs are today performed by specialist hand surgeons working closely with hand therapists.
Each of Verdans flexor tendon zones has a unique set of anatomical considerations which the surgeon must be aware of.
The following technique demonstrates repair of a zone II laceration of flexor digitorum profundus (FDP).
This zone extends from the proximal margin of the A1 pulley to the insertion point of flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS). The zone is characterised by a tight fibro-osseous tunnel with closely related pulleys and a complex interweaving of tendons.
Sterling Bunnel called this area ‘no mans land’ alluding to the difficulty of primary repair here and historical results of attempted repair were all too often compromised by infection, dense scarring and loss of motion. Early surgeons therefore favoured acute wound closure and secondary tendon grafting of FDP. In the late 1960s however Kleinerts group published 87% good to excellent results of flexor tendon repair and this lead to a resurgence of primary repair.
The use of prophylactic antibiotics no doubt contributed to improved early results. However over recent decades, further refinements including the routine use of magnification, meticulous tissue handling, robust suture techniques and improved rehabilitation protocols, have all contributed to improved results of repair for these potentially devastating injuries.
Today multiple techniques of flexor tendon repair are in use according to individual surgeon preference. Each technique aims to appose the tendon ends with minimal gapping and a smooth repair site with preservation of tendon vascularity, and adequate strength to withstand rehabilitation protocols.
Readers will also find the following techniques on OrthOracle of interest:
First stage flexor tendon reconstruction
Flexor tendon reconstruction: Second stage.
Reattachment of Flexor digitorum profundus tendon
Author: Tahseen Chaudhry, Consultant in Hand and Peripheral Nerve Surgery
Institution: Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK
Clinicians should seek clarification on whether any implant demonstrated is licensed for use in their own country.
In the USA contact: fda.gov
In the UK contact: gov.uk
In the EU contact: ema.europa.eu
Online learning is only available to subscribers.