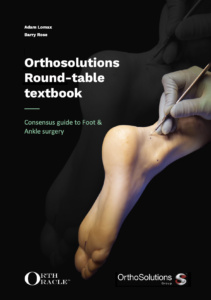
Infected femoral nail removal and debridement with Synthes Reamer Irrigator Aspirator (RIA)
Overview
Subscribe to get full access to this operation and the extensive Hip Surgery Atlas.
Professional Guidelines Included
Learn the Infected femoral nail removal and debridement with Synthes Reamer Irrigator Aspirator (RIA) surgical technique with step by step instructions on OrthOracle. Our e-learning platform contains high resolution images and a certified CME of the Infected femoral nail removal and debridement with Synthes Reamer Irrigator Aspirator (RIA) surgical procedure.
Fracture related infection (FRI) has a spectrum of presentations ranging from early and obvious infection after fracture fixation to delayed presentations with infected non-union of fractures. Its incidence is reported as being between 1-30% of fractures and is more common following open injuries. FRI has various potential aspects to its presentation and management, including bone infection, soft tissue injury, fractures in varying states of healing and metalwork with biofilm. There is currently a lack of high quality evidence to guide practice in this area and there have been a number of recent consensus papers and a BOAST guideline in an attempt to define best practice.
Diagnostic criteria considered to confirm FRI include a sinus, fistula or wound breakdown over bone or implant, purulent discharge or pus found during surgery, phenotypically indistinguishable pathogens from 2 deep samples or histopathological staining for bacteria or fungi. Criteria suggestive of FRI include clinical signs of local inflammation (pain, swelling, redness, temperature), radiological signs (lysis, implant loosening, sequestration, periosteal bone formation), elevated blood markers (WBC, CRP, ESR) or a pathogenic organism grown from a single deep tissue sample.
RIA is made by Synthes, as the name suggests it simultaneously reams, aspirates and irrigates the intramedullary canal as it is passed.
It can be used simply to harvest autologous bone graft for reconstruction cases however it also allows simultaneous reaming of infected material with irrigation as the reamer passes and collection of the reamings to remove and sample infected tissues in infected cases. RIA is not routinely used for primary nailing of fractures as there is an advantage to autografting the fracture site with reamings rather than removing them.
Author: Paul Fenton FRCS (Tr & Orth)
Institution: The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham UK.
Clinicians should seek clarification on whether any implant demonstrated is licensed for use in their own country.
In the USA contact: fda.gov
In the UK contact: gov.uk
In the EU contact: ema.europa.eu
Online learning is only available to subscribers.