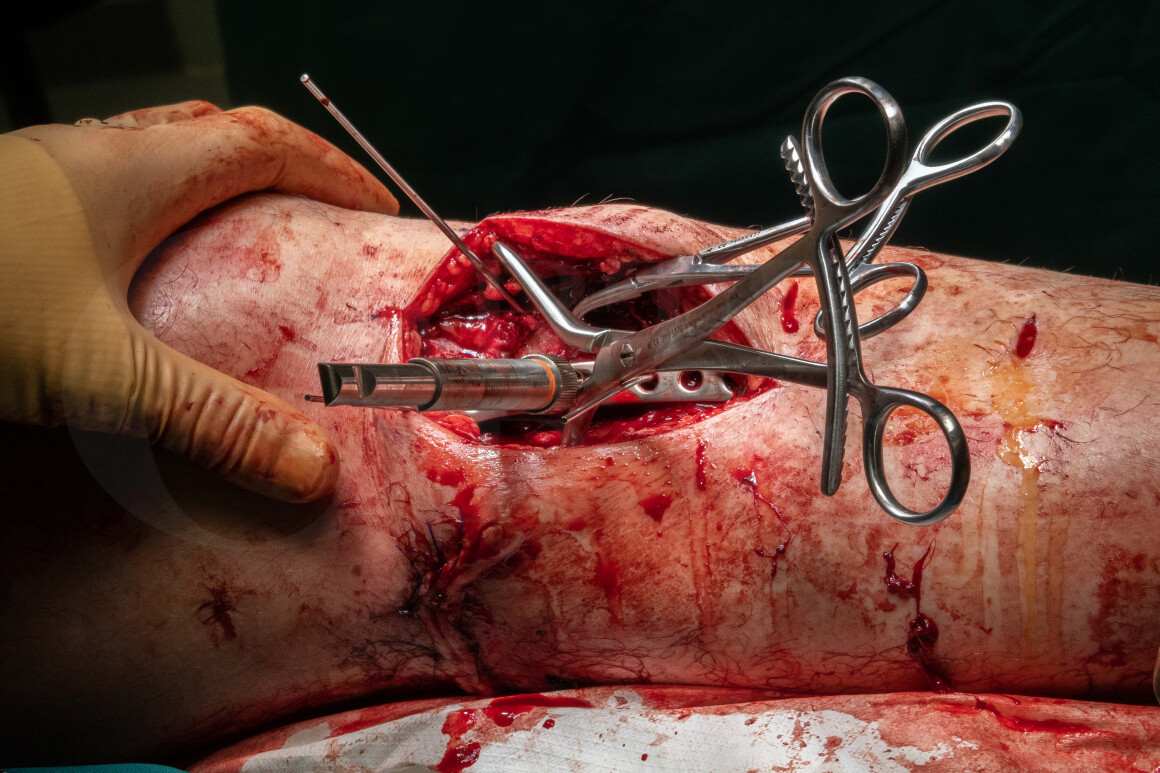
Tibial plateau fracture: Fixation of a bicondylar fracture with a dual incision technique (Smith and Nephew EVOS plates)
Overview
Subscribe to get full access to this operation and the extensive Knee Surgery Atlas.
Learn the Tibial plateau fracture: Fixation of a bicondylar fracture with a dual incision technique (Smith and Nephew EVOS plates) surgical technique with step by step instructions on OrthOracle. Our e-learning platform contains high resolution images and a certified CME of the Tibial plateau fracture: Fixation of a bicondylar fracture with a dual incision technique (Smith and Nephew EVOS plates) surgical procedure.
As with much of adult trauma tibial plateau fractures have a bimodal distribution. In younger patients these injuries result from high energy mechanisms such as falls from height or road traffic accidents whereas in the elderly population they more often result from simple falls.
Tibial plateau injuries have been classified by Schatzker, on the basis of plain film radiographs, into 6 types. Types 5 (bicondylar) and type 6 (bicondylar with complete separation of the joint surface from the tibial shaft) represent the higher energy injuries. A more recent classification by Luo, based on CT scans, divides the tibial plateau into 3 columns, medial, lateral and posterior and helps to guide the surgical approach to the fracture depending on the precise fracture configuration.
The majority of tibial plateau fractures involve the lateral side and can be approached with the standard anterolateral approach with meniscal elevation. For those fractures with medial or posterior involvement a number of further approaches are possible from direct medial, postero-medial, direct posterior or even poster-lateral.
Fixation of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures was previously performed via a single anterior mid-line incision however concerns with high rates of soft tissue complications and deep infection rates of over 20% associated with this approach led to a change in the management of these injuries. From the early 2000’s authors such as Barei and Egol (see below) popularised a staged approach to high energy bicondylar tibial plateau fractures with initial spanning external fixation to resuscitate the soft tissues followed by internal fixation utilising dual incisions to minimise soft tissue stripping, this led to a reduction in infection rates to below 10%.
The Smith and Nephew EVOS plates are anatomical plates for the anterolateral and medial proximal tibia. They have a good anatomical fit that minimises soft tissue irritation. The implants come as either complete articular (thicker plates with fixed angle locking screw holes in the diaphysis, intended for bridge plating) or partial articular (thinner plates with variable angle locking options in the diaphysis suited to buttress plating). The plates have a range of options for peri-articular screw placement allowing flexibility in screw positioning to “raft” beneath the joint surface.
It should be noted however, that whilst the use of anatomical locking plates for peri-articular fractures is convenient it is not mandatory and the principles of fixation of these injuries, which is anatomic reduction and absolute stability of the articular block with a relative stability construct for the metaphyseal/diaphyseal component of the injury, can be achieved just as readily with standard locking compression plates.
OrthOracle readers will also find the following techniques of interest:
Tibial plateau fracture: Posterior column fracture fixed with Synthes proximal tibial LISS plate
Tibial Plateau Fracture: Sleeved MBT(DePuy) Total Knee Replacement
Compartment fasciotomy and Hoffmann 3 spanning external fixator for open tibial fracture
Author: Paul Fenton FRCS (Tr & Orth).
Institution: The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham, UK.
Clinicians should seek clarification on whether any implant demonstrated is licensed for use in their own country.
In the USA contact: fda.gov
In the UK contact: gov.uk
In the EU contact: ema.europa.eu
Online learning is only available to subscribers.