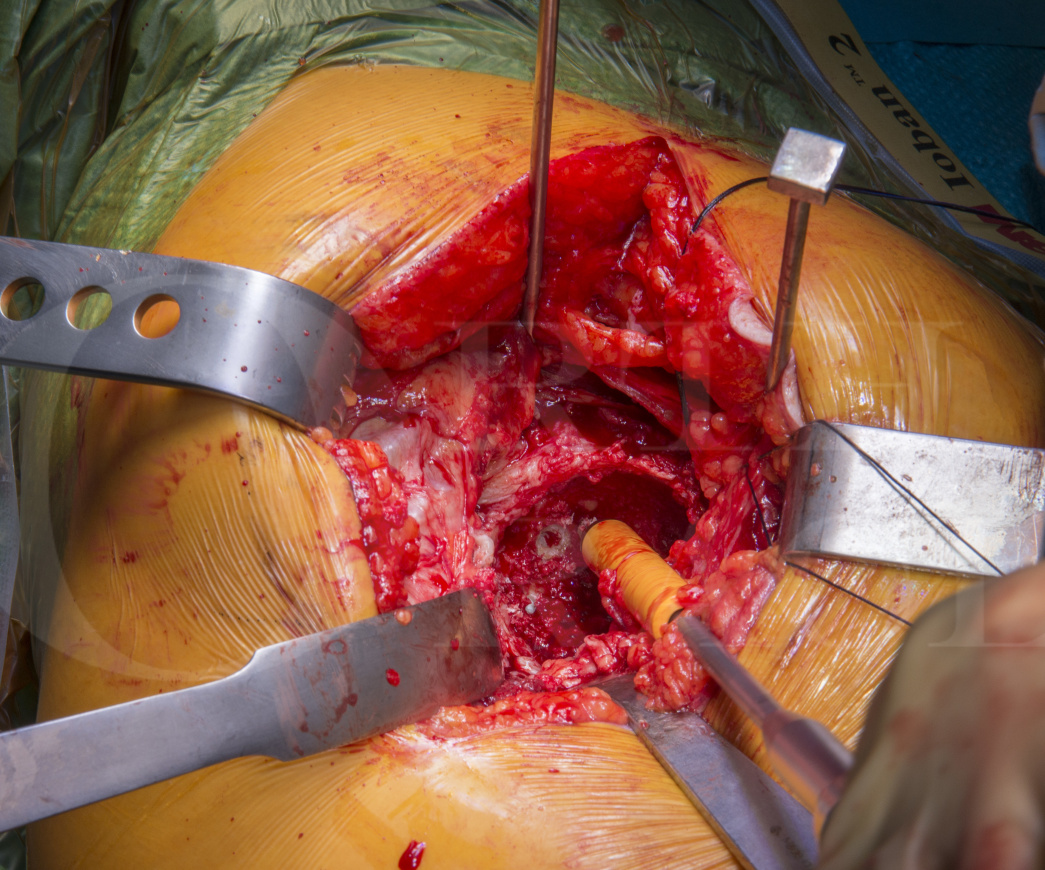
Total Hip replacement(posterior approach): Cemented Exeter/Contemporary (Stryker)
Overview
Subscribe to get full access to this operation and the extensive Hip Surgery Atlas.
Learn the Total Hip replacement(posterior approach): Cemented Exeter/Contemporary (Stryker) surgical technique with step by step instructions on OrthOracle. Our e-learning platform contains high resolution images and a certified CME of the Total Hip replacement(posterior approach): Cemented Exeter/Contemporary (Stryker) surgical procedure.
A cemented total hip replacement should be considered in the elderly population. It is forgiving to the ageing skeleton which is reflected in the fact that there is a lower risk of fracture of both the acetabular and femoral bone when compared to uncemented designs.
The Exeter cemented stem has excellent survivorship, reported as 100% at 17 years (Carrington et al), and is a polished, double tapered cemented stem which has an ODEP* 13A star rating.
The contemporary cup has excellent survival (Magges et al). Options for both a ceramic or metal head are available and where possible a 32mm head is favoured to reduce dislocation rates.
Carrington et al. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009 Jun;91(6):730-7.
The first 325 Exeter Universal stems implanted at the originating centre were reviewed, and using an endpoint
of revision for aseptic loosening, the survivorship at 17 years was 100% and 90% for the femoral and acetabular component, respectively. Radiological review showed excellent preservation of bone stock in the proximal femur and no failures of the femoral component.
Maggs et al. Bone Joint J. 2016 Mar;98-B(3):307-12.
This study reviewed 203 hips in 194 patients. There were no acetabular component revisions for aseptic loosening. Kaplan-Meier survivorship, with revision for aseptic loosening as the endpoint, was 100% at 12.5 years.
Author: Mr Richard Baker MD, MSc, MB.ChB, FRCS (Tr & Orth)
Institution: The Avon Orthopaedic Centre, Bristol, UK.
Clinicians should seek clarification on whether any implant demonstrated is licensed for use in their own country.
In the USA contact: fda.gov
In the UK contact: gov.uk
In the EU contact: ema.europa.eu