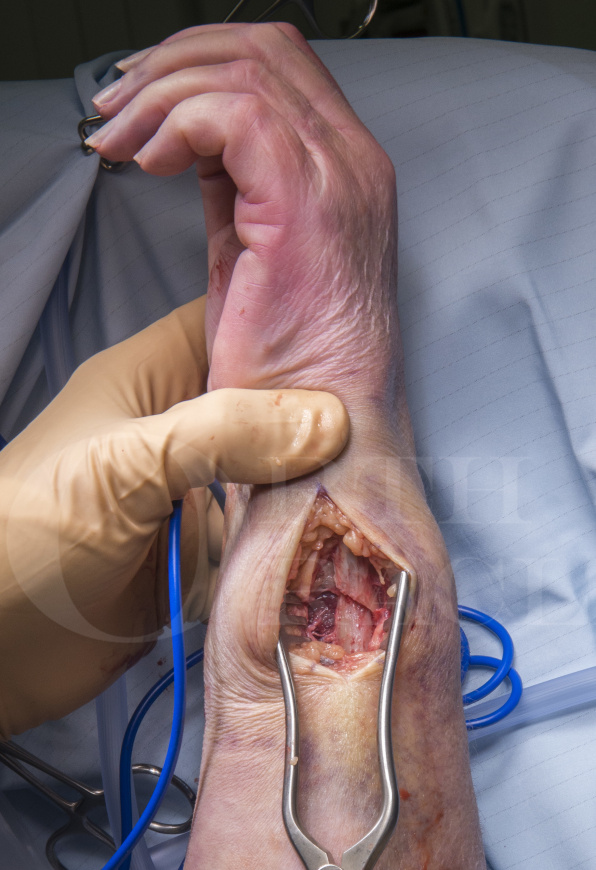
Distal ulna fracture fixation using the Synthes 2mm LCP Distal Ulna Plate
Overview
Subscribe to get full access to this operation and the extensive Upper Limb & Hand Surgery Atlas.
Learn the Distal ulna fracture fixation using the Synthes 2mm LCP Distal Ulna Plate surgical technique with step by step instructions on OrthOracle. Our e-learning platform contains high resolution images and a certified CME of the Distal ulna fracture fixation using the Synthes 2mm LCP Distal Ulna Plate surgical procedure.
Distal ulna fractures rarely occur in isolation and are usually associated with a distal radius fracture. Combined distal radius and distal ulna fractures in adults typically present in the elderly (> 65 years old) and are associated with osteoporosis. Ulnar styloid tip fractures are very common and are associated with 55% of distal radius fractures. The majority of these are stable and are treated conservatively. Ulnar metaphyseal fractures are less common and are only associated with 5-6% of distal radius fractures.
With the wrist in neutral rotation, the ulnocarpal joint bears nearly 20% of the load across the wrist. As the forearm rotates into pronation or when gripping, there is a relative increase in ulnar length and the proportion of load transfer through the ulnocarpal joint will increase.
The distal ulna can be subdivided into three regions. The ulnar styloid tip, the ulnar styloid base / ulnar head, and the distal ulnar metaphysis. The ulnar styloid is the anchor for the Triangular FibroCartilage Complex (TFCC) and the ulnocarpal ligaments. The TFCC preserves the congruence between the distal radius and ulnar head; and the proximal carpal row. The TFCC has superficial and deep components. The superficial ligaments are attached to the ulnar styloid tip, and the deep fibres are attached to the fovea of the ulnar head at the base of the ulnar styloid.
A distal ulnar metaphysis fracture can be defined as a fracture that is within 5cm of the distal ulnar dome of the ulnar head.
The stability of the DRUJ is determined by the bony anatomy (and the shape of the sigmoid notch of the distal radius), and the surrounding ligaments and muscles. The stabilising structures are the:
- Triangular FibroCartilage Complex (TFCC)
- Ulnocarpal ligament complex
- Extensor Carpi Ulnaris (ECU) tendon and tendon sheath
- Pronator Quadratus (PQ) muscle
- Interosseous membrane (IOM) and the interosseous ligament (IOL)
- Joint capsule
The Synthes 2.0mm Locking Compression Plate for Distal Ulna fractures is indicated for ulnar styloid and ulnar head / neck fractures. The plate is anatomically contoured with a low profile which reduces the need for extensive soft tissue dissection and lowers the incidence for implant removal due to soft tissue irritation. The plate accepts both non-locking and fixed angle locking screws via Combi holes in the plate shaft section. Using non-locking screws in the shaft section allows for length adjustment and/or dynamic fracture compression. Distally on the under-surface of the implant, there is a cut on the plate which allows for contouring if necessary. The distal section only accepts locking screws which provide angular stability and in combination with the hook section provide good fixation to an often very small fracture fragment. The hook section also allows the plate to be applied in the correct position and gives a good indication for reference height and plate positioning. Between the prongs of the hook, a 1.1mm K-wire can be used to temporarily hold the reduction or it can be exchanged for a 1.5mm non-locking screw that can be used to stabilise a styloid tip fracture.
Readers will also find of interest these other associated OrthOracle surgical techniques:
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of a Galeazzi radius fracture using Synthes LCP locking plate
Distal radius fracture : Manipulation Under Anaesthetic (MUA) and K-wire fixation
Compound distal radius fracture: stabilised with Hoffman II External Fixator
Distal Radius Fracture fixation , volar approach with Synthes® 2.4 mm Variable Angle locking LCP
Distal Radial fracture fixation with dorsal approach and Synthes 2.4mm variable angle plating system
Author: Mr Ross Fawdington FRCS (Tr & Orth)
Institution: The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham, UK.
Clinicians should seek clarification on whether any implant demonstrated is licensed for use in their own country.
In the USA contact: fda.gov
In the UK contact: gov.uk
In the EU contact: ema.europa.eu
Online learning is only available to subscribers.