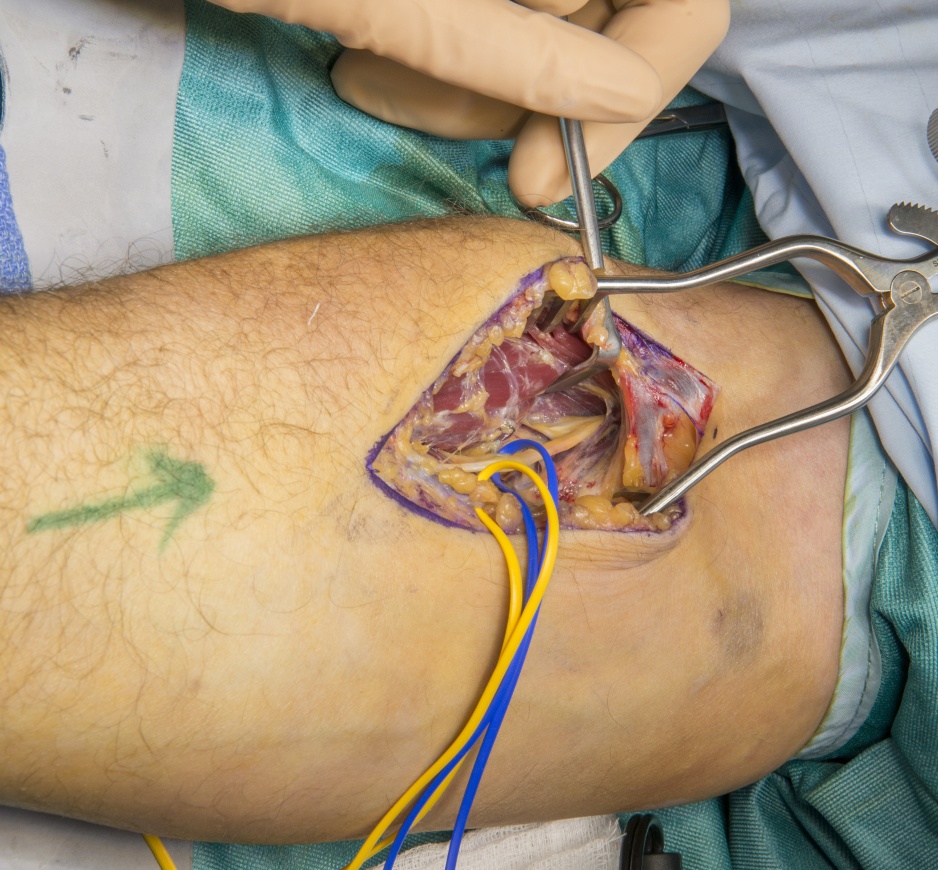
Supinator to Posterior Interosseous Nerve Transfer (S-PIN transfer)
Overview
Subscribe to get full access to this operation and the extensive Upper Limb & Hand Surgery Atlas.
Learn the Supinator to Posterior Interosseous Nerve Transfer (S-PIN transfer) surgical technique with step by step instructions on OrthOracle. Our e-learning platform contains high resolution images and a certified CME of the Supinator to Posterior Interosseous Nerve Transfer (S-PIN transfer) surgical procedure.
Motor nerve transfer surgery uses an expendable nerve branch or redundant nerve fascicle from within a functioning nerve to transfer directly to the terminal motor branch of a paralysed muscle with a more important function. The nerve co-aptation is close to the target muscle and reinnervation distances are therefore short. The Supinator to Posterior Interosseus nerve transfer (S-PIN transfer) is indicated in isolated lower brachial plexus injuries (C8/T1), degenerate C8 motor radiculopathy or in mid-cervical tetraplegia. The aim is to restore digit extension using medial and lateral branches of the PIN to supinator innervated from the C6 root. These branches are implanted to the adjacent PIN (C8 digit extension) through either an anterior or a posterior approach to the PIN. The supinator is decompressed as part of the procedure when performed through the anterior approach and this technique is illustrated here.
Author: Dominic Power FRCS Orth, Consultant Hand and Peripheral Nerve Surgeon
Institution: Peripheral Nerve Injury Service, Birmingham Hand Centre, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, UK
Clinicians should seek clarification on whether any implant demonstrated is licensed for use in their own country.
In the USA contact: fda.gov
In the UK contact: gov.uk
In the EU contact: ema.europa.eu
Online learning is only available to subscribers.