Targeted Muscle Reinnervation (TMR) for neuroma treatment following above knee amputation
Overview
Subscribe to get full access to this operation and the extensive Upper Limb & Hand Surgery Atlas.
Learn the Targeted Muscle Reinnervation (TMR) for neuroma treatment following above knee amputation surgical technique with step by step instructions on OrthOracle. Our e-learning platform contains high resolution images and a certified CME of the Targeted Muscle Reinnervation (TMR) for neuroma treatment following above knee amputation surgical procedure.
There are various potential sources of chronic nerve pain following amputation but approximately one quarter of lower limb amputees will develop chronic nerve pain specifically due to a symptomatic neuroma within the stump. Chronic nerve pain is a major source of disability in some patients following limb amputation, reducing engagement with rehabilitation programmes and tolerance of prosthetic use. There is an accompanying burden of psychosocial morbidity.
Treatment of symptomatic neuromas is a challenge for the whole pain team as well as the peripheral nerve surgeon.
Various surgical techniques are described, and varying degrees of success reported for each.
During lower limb amputation surgery peripheral nerves are often divided under traction, allowing them to retract away from the stump into healthier tissue. This method however can lead to neuroma formation with spontaneous and evoked pain as well as allodynia, hyperalgesia and dysaesthesia, hallmarks of central sensitisation.
Surgical treatment for an end neuroma may involve use of a capping device, burial of the stump within muscle or within a cortical bone window or anastomosis to another nerve or a a long nerve ‘graft to nowhere’. Results of these techniques are inconsistent, and treatment of these patients remains difficult.
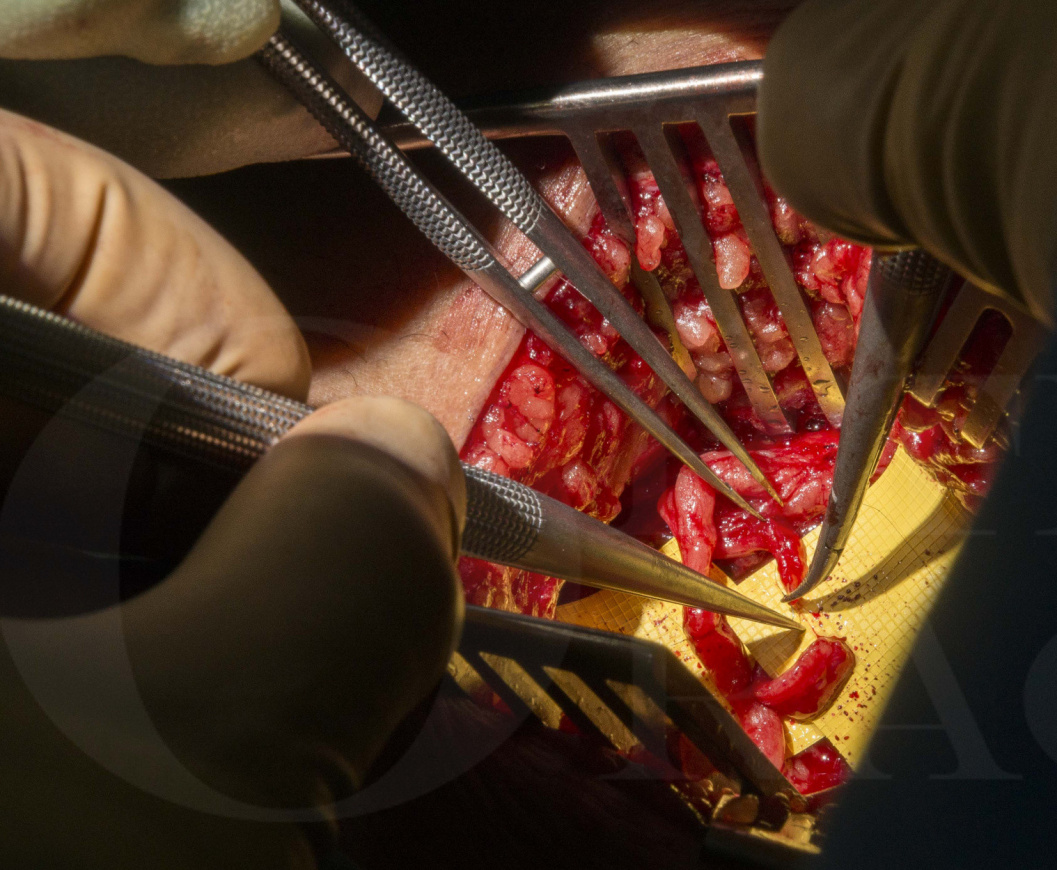
Targeted muscle reinnervation (TMR) involves a nerve transfer of the residual nerve end to a motor nerve that is no longer useful. This is performed as close as possible to its entry point into the muscle.
TMR has shown success in the upper limb where it has been used to generate physiologically appropriate electromyography signals within muscles of the residual limb for prosthetic control. Significant reductions in neuroma pain have also been noted in these patients.
Early results of TMR in the lower limb have shown promise in preventing or treating neuroma pain. It may be offered at the time of amputation as a preventative measure, or in the treatment of established, symptomatic neuroma in an amputation stump.
Coapting sectioned nerve stumps onto recipient motor nerve branches encourages nerve regeneration into the target muscle, preventing the formation or recurrence of neuroma.
In this section the workup and surgical technique in a patient with an established end neuroma following an above knee amputation stump is described.
Readers will also find the following OrthOracle surgical techniques of interest:
Excision of a sural nerve end neuroma and application of a Polyganics NeuroCapTM
Author: Tahseen Chaudhry, Consultant hand and peripheral nerve surgeon
Institution: University Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK
Clinicians should seek clarification on whether any implant demonstrated is licensed for use in their own country.
In the USA contact: fda.gov
In the UK contact: gov.uk
In the EU contact: ema.europa.eu
Online learning is only available to subscribers.