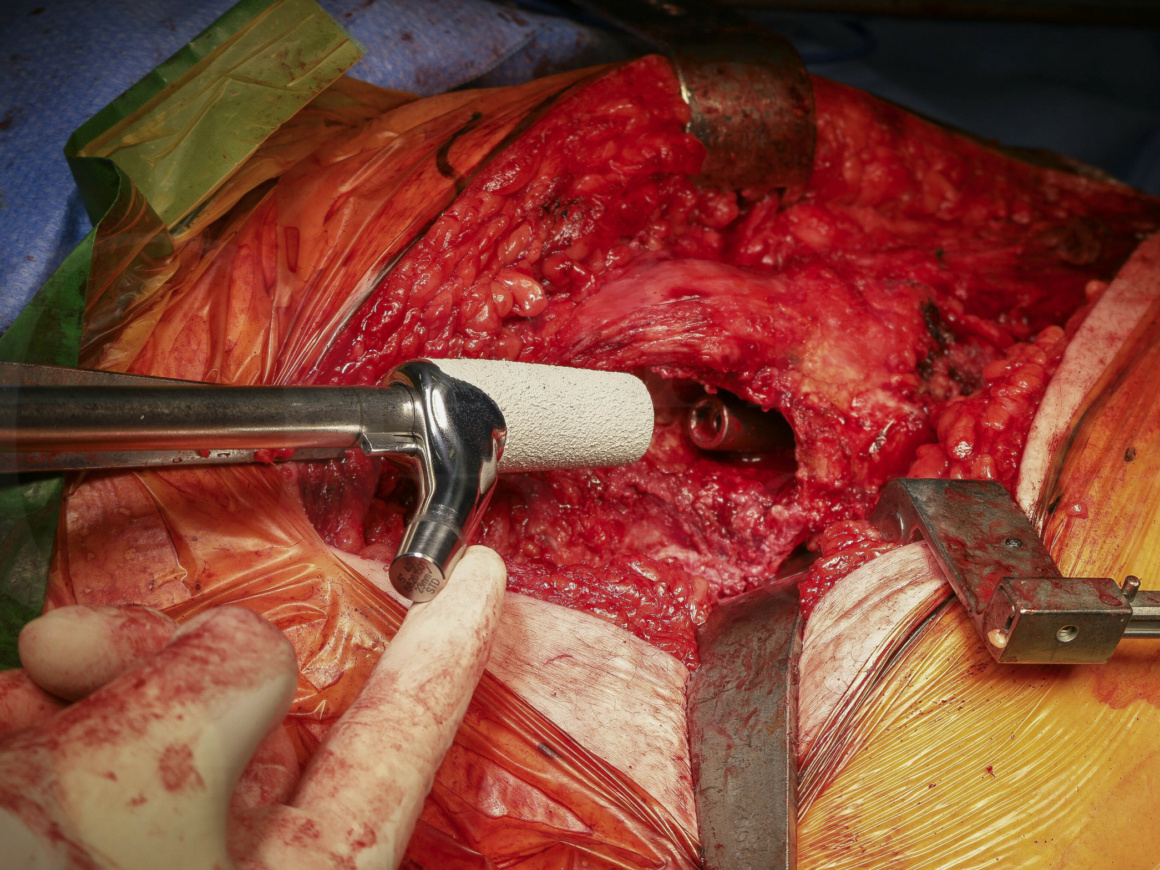
Revision Hip replacement: Femoral revision with an uncemented Restoration Modular stem(Stryker) utilising a lateral cortical window
Overview
Subscribe to get full access to this operation and the extensive Hip Surgery Atlas.
Learn the Revision Hip replacement: Femoral revision with an uncemented Restoration Modular stem(Stryker) utilising a lateral cortical window surgical technique with step by step instructions on OrthOracle. Our e-learning platform contains high resolution images and a certified CME of the Revision Hip replacement: Femoral revision with an uncemented Restoration Modular stem(Stryker) utilising a lateral cortical window surgical procedure.
The Exeter Universal cemented femoral component (Stryker, Newbury, UK) is currently the most commonly used cemented total hip replacement (THR) prosthesis in the UK and probably worldwide. Its popularity is justified by the many excellent longterm outcomes published using the implant. There have however been few reports of fracture of the femoral component in the literature, mainly related to revision or older component design, as published by Van Doorn and Røkkum.
Risk factors for stem breakage can be divided into patient or implant factors. Patient factors include weight, bone density, age and activity level. Factors affecting the implant such as cementing technique and a small cross-sectional area of the stem can also contribute to failure. Myself and co-authors have also published a series of triple taper polished cemented stems presenting with fatigue failure related to the stem design and bone loss, but this is my first revision of a fractured Exeter stem.
Buttaro M, Comba F, Zanotti G, Piccaluga F. Fracture of the C-Stem cemented femoral component in revision hip surgery using bone impaction grafting technique: report of 9 cases. Hip Int. 2015;25(2):184-7.
Removal of the distal part of a fractured stem is always a challenging situation in revision THA. If the fractured femoral component is well-fixed the technical challenge is even more demanding and often risks significant detrimental effect to the remaining host bone.
The benefits of cortical windows are that this technique also allows for easy removal of distal cement mantle or, as in this case, the distal part of a broken cemented stem. Moreover, the osteotomy can be easily fixed with several cerclage wires, it does not compromise the abductor mechanism because it is distal, and the patient does not need to limit weight bearing. Importantly in terms of achieving primary stability of the revision implant the femoral stem can be fixed to an intact greater trochanter, which is not possible if an extended trochanteric osteotomy (ETO) is performed.
The following technique provides an easy method of windowing the femur, facilitating cement removal and firm fixation of the new prosthesis, in this case, an uncemented, distally fixed, Restoration Modular TM stem.
Van Doorn WJ, van Biezen FC, Prendergast PJ, Verhaar JA. Fracture of an Exeter stem 3 years after impaction allografting – a case report.
Acta Orthop Scand 2002; 73: 111–113;
Røkkum M, Bye K, Hetland KR, Reigstad A. Stem fracture with the Exeter prosthesis. 3 of 27 hips followed for 10 years.
Acta Orthop Scand 1995; 66: 435–439.
OrthOracle readers will also find the following instructional operative techniques of interest:
Revision total hip replacement: DePuy Reclaim stem and extended trochanteric osteotomy
Revision Total Hip replacement: Direct exchange Link MP revision stem for periprosthetic fracture
Author: Martin Buttero MD
Institution: Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Clinicians should seek clarification on whether any implant demonstrated is licensed for use in their own country.
In the USA contact: fda.gov
In the UK contact: gov.uk
In the EU contact: ema.europa.eu