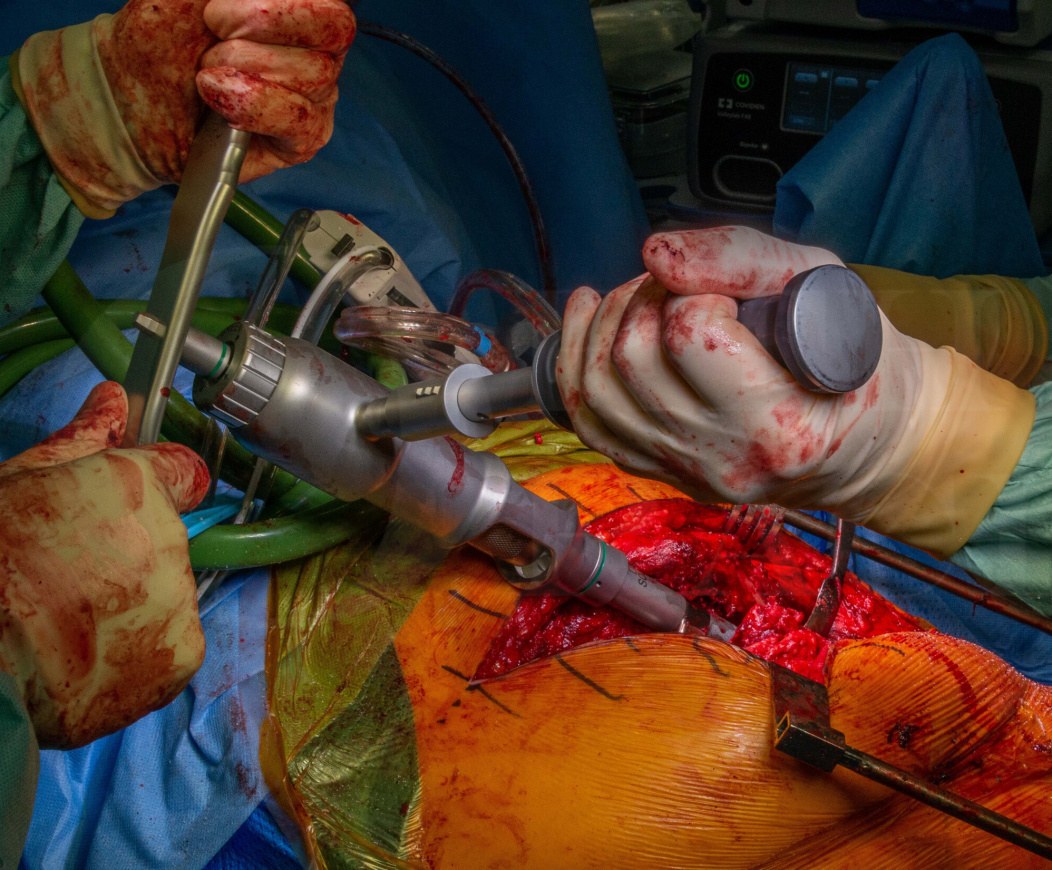
Revision total hip replacement: DePuy Reclaim stem and extended trochanteric osteotomy
Overview
Subscribe to get full access to this operation and the extensive Hip Surgery Atlas.
Learn the Revision total hip replacement: DePuy Reclaim stem and extended trochanteric osteotomy surgical technique with step by step instructions on OrthOracle. Our e-learning platform contains high resolution images and a certified CME of the Revision total hip replacement: DePuy Reclaim stem and extended trochanteric osteotomy surgical procedure.
Modular revision hip stems are increasingly popular and offer the benefit of distal fixation whilst maintaining the flexibility to modify offset, leg length and version. They have a relatively high re-revision rate in the early post-operative period and this may be due to undersizing, peri-prosthetic fracture or an early complication such as instability or infection. In the longer term they out-perform cemented stems and hence their ongoing use.
This case demonstrates early loosening of a Zimmer ZMR modular tapered revision stem in a 65 year old male patient. The patient is somewhat unusual in that he had the primary long-stem replacement for a proximal femoral fracture non-union. He also suffers from multiple medical and psychological issues.
An extended trochanteric osteotomy (ETO) is performed to enhance proximal femoral access and to facilitate the insertion of a new stem. This allows a “straight shot” down the femoral canal and reduces the risk of undersizing, varus malposition or anterior cortical perforation of the femur. I find it especially useful where the proximal femur has remodelled in varus.
The DePuy Reclaim revision stem allows initial distal fixation independently of the proximal femur and then subsequent reconstruction with differing neck lengths and offset. The taper has been engineered to allow it to function as a proximal femoral replacement if the medial bone is compromised.
The Reclaim stem (or other modular tapered fluted revision stem) is often used in Paprosky type 2-3 cases and in some type 4 defects.
Infection was excluded with inflammatory markers, SPECT CT and an image guided biopsy. It is standard practice in our unit to discuss all upcoming revision arthroplasty cases in an MDT setting.
OrthOracle readers will also find the following associated instructional techniques of interest:
Revision total hip replacement: Using MUTARS proximal femoral endoprosthesis (Implantcast)
Revision Total Hip replacement: Direct exchange Link MP revision stem for periprosthetic fracture
Revision Total Hip replacement: Stryker custom acetabulum and SERF Dual mobility Hip (De Puy)
Author: James Donaldson FRCS(Tr and Orth)
Institution: The Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, Stanmore, London, UK.
Clinicians should seek clarification on whether any implant demonstrated is licensed for use in their own country.
In the USA contact: fda.gov
In the UK contact: gov.uk
In the EU contact: ema.europa.eu
Online learning is only available to subscribers.